-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Board: LimiFrog v1
LimiFrog-v1 arose from the La BlueFrog board. LimiFrog-v1 contains the first hardware revision. LimiFrog-v2 will follow. LimiFrog features a variety of sensors as well as an OLED Display and a BLE (Bluetooth Low-Energy) module.

| MCU | STM32L151RC |
|---|---|
| Family | ARM Cortex-M3 |
| Vendor | ST Microelectronics |
| RAM | 32Kb |
| Flash | 256Kb |
| Frequency | 32MHz (no external oscilator connected) |
| FPU | no |
| Timers | 8 (8x 16-bit, 1x 32-bit [TIM5]) |
| ADCs | 1x 42-channel 12-bit |
| UARTs | 3 |
| SPIs | 2 |
| I2Cs | 2 |
| Vcc | 1.65V - 3.6V |
| Datasheet | Datasheet |
| Reference Manual | Reference Manual |
| Programming Manual | Programming Manual |
2 Buttons:
| PIN |
|---|
| PA15 (IN) |
| PC8 (IN) |
1 LED:
| NAME | LED_RED |
|---|---|
| Color | red |
| Pin | PC3 |
| Device | ID | Supported | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCU | STM32L151RC | partly | Energy saving modes not fully utilized |
| Low-level driver | GPIO | yes | |
| PWM | yes | ||
| UART | yes | ||
| I2C | yes | ||
| SPI | yes | ||
| Timer | yes | ||
| Ambient Light Sensor | ST VL6180X | no | planned |
| Accelerometer | ST LSM6DS3 | no | planned |
| Magnetometer | ST LIS3MDL | no | planned |
| Gyroscope | ST LSM6DS3 | no | planned |
| atmospheric pressure (and altitude) sensor | ST SLPS25H | no | planned |
| Microphone | Knowles SPU0414HR5H-SB | no | planned |
| OLED Display | Densitron DD-160128FC-1A | no | planned |
| BLE | Panasonic PAN1740 | no | planned |
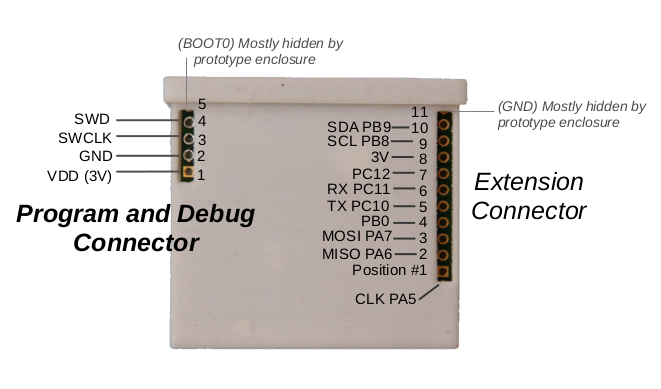
The LimiFrog-v1 has no on-board programmer nor an USB-UART converter. It can be programmed by using the integrated ST-Link/V2 programmer of any STM32Fx-discovery board. See [here] (https://github.com/RIOT-OS/RIOT/wiki/Board%3A-yunjia-nrf51822#flashing-and-debugging) for an example. Another way is to use a stand-alone ST-Link V2 programmer as shown in the picture.
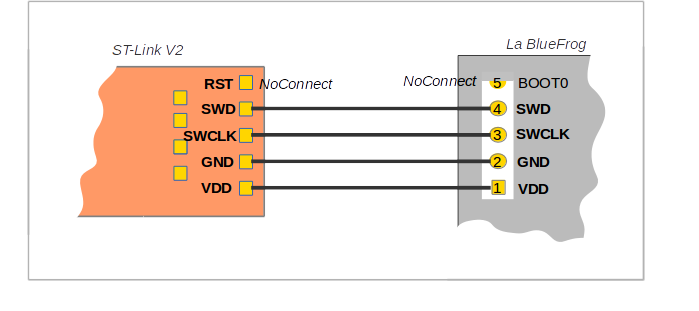
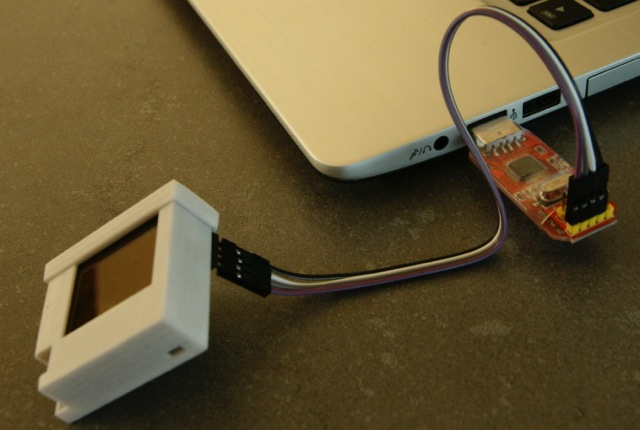
To debug the device you may also want to use a stand-alone UART converter and connect it to the pins PC10 and PC11 and keep the programmer plugged.
RIOT - The friendly Operating System for the Internet of Things
Homepage | [GitHub] (https://github.com/RIOT-OS/) | Developers Mailing List | Users Mailing List | Twitter @RIOT_OS
- Family: ARM
- Board: Airfy Beacon
- Board: Arduino Due
- Board: CC2538DK
- Board: CC2650STK
- Board: HikoB Fox
- Board: IoT LAB M3
- Board: LimiFrog-v1
- Board: mbed_lpc1768
- Board: MSB-IoT
- Board: MSBA2
- Board: Nucleo-L1
- Board: Nucleo-F446
- Board: Nucleo-F334
- Board: Nucleo-F303
- Board: Nucleo-F091
- Board: Mulle
- Board: OpenMote
- Board: PCA1000x (nRF51822 Development Kit)
- Board: Phytec phyWAVE-KW22
- Board: RFduino
- Board: SAMR21-xpro
- Board: SAML21-xpro
- Board: Seeeduino Arch-Pro
- Board: SODAQ Autonomo
- Board: Spark Core
- Board: STM32F0discovery
- Board: STM32F3discovery
- Board: STM32F4discovery
- Board: UDOO
- Board: yunjia-nrf51822
- Board: Zolertia remote
- Family: ATmega
- Board: Arduino Mega2560
- Board: Arduino Uno
- Board: Arduino Duemilanove
- Family: MSP430
- Board: MSB-430H
- Board: TelosB
- Board: WSN430
- Board: Zolertia Z1
- Board: eZ430-Chronos
- Family: native
- Board: native
- Family: x86
- Board: Intel Galileo