| author | title | date | logo | footnote | header-includes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ISTD, SUTD |
Spark (Part 2) |
Feb 27, 2023 |
\usepackage{tikz}
\usetikzlibrary{positioning}
\usetikzlibrary{arrows}
\usetikzlibrary{shapes.multipart}
|
By the end of this lesson, you are able to
- Explain Spark Architecture
- Develop Data processing application using Spark Dataframe
- Develop Machine Learning application using Spark ML package
- Explain Spark Streaming
Looks familiar?
- Inspired by Panda's dataframe
- Built mainly for structured data
- A main pipeline in Machine Learning,
- Unstructured data -> structured data -> models
- Schema + RDD
- Internally Columar Storage
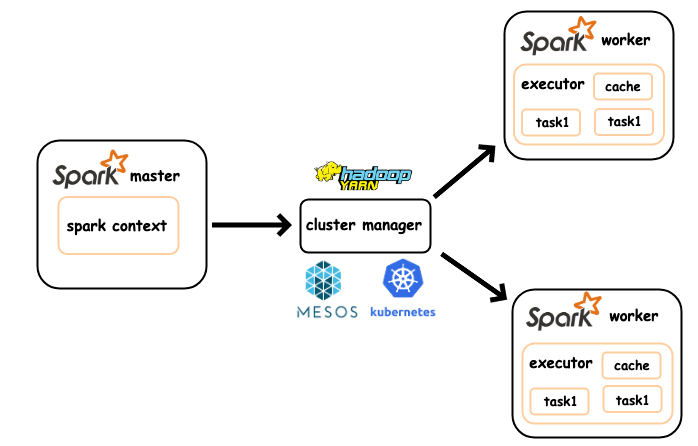
 {width=50%}
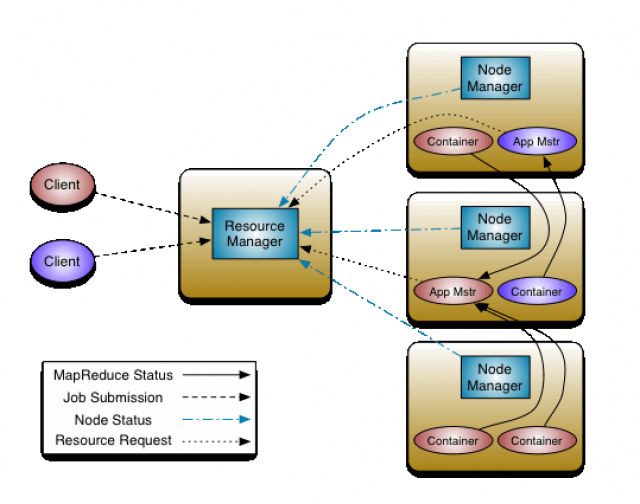
{width=50%}
df = rdd.toDF("colname1", "colname2")
df = sc.createDataFrame(rdd, schema)
rdd = df.rddGiven
foo,bar
1,true
2,false
3,true
4,false
df = sparkSession.read\
.option("header", "true")\
.option("inferSchema", "true")\
.csv("hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/foo.csv")
df.printSchema()shows
root
|-- foo: integer (nullable = true)
|-- bar: boolean (nullable = true)
Given
{ "foo":1, "bar":true }
{ "foo":2, "bar":false }
{ "foo":3, "bar":true }
{ "foo":4, "bar":false }df2 = sparkSession.read\
.option("inferSchema", "true")\
.json("hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/foo.json")
df2.printSchema()shows
root
|-- bar: boolean (nullable = true)
|-- foo: long (nullable = true)
Given
{ "foo":1, "bar":true }
{ "foo":2, "bar":false }
{ "foo":[3,4], "bar":true }
{ "foo":4, "bar":false }df3 = sparkSession.read\
.option("inferSchema", "true")\
.json("hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/foo2.json")
df3.printSchema()shows
root
|-- bar: boolean (nullable = true)
|-- foo: string (nullable = true)
foo's type changes from long to string? hm....
df3 = sparkSession.read\
.option("inferSchema", "true")\
.json("hdfs://127.0.0.1:9000/foo2.json")
df3.show()shows
+-----+-----+
| bar| foo|
+-----+-----+
| true| 1|
|false| 2|
| true|[3,4]|
|false| 4|
+-----+-----+
Best effort only!
- Column Projection
- Column Conversion
- Row Filtering
- Grouping and Aggregation
- Joining
data = [("100001", "Ace", "50043", 90), \
("100002", "Brandon", "50043", 95), \
("100003", "Cheryl", "50043", 80)]
distData = sc.parallelize(data)
df = distData.toDF(["studentid", "name", \
"module", "score"])
df.show(5)+---------+-------+------+-----+
|studentid| name|module|score|
+---------+-------+------+-----+
| 100001| Ace| 50043| 90|
| 100002|Brandon| 50043| 95|
| 100003| Cheryl| 50043| 80|
+---------+-------+------+-----+
df.select(df["studentid"], df["score"]).show() # or
from pyspark.sql.functions import col
df.select(col("studentid"), col("score")).show() +---------+-----+
|studentid|score|
+---------+-----+
| 100001| 90|
| 100002| 95|
| 100003| 80|
+---------+-----+
from pyspark.sql.functions import concat, lit
df.select(concat(df["studentid"]\
,lit("@mymail.sutd.edu.sg"))\
.alias("email")).show()+--------------------+
| email|
+--------------------+
|[email protected]...|
|[email protected]...|
|[email protected]...|
+--------------------+
To see the full list of builtin funtcions.
- Python
pyspark.sql.functions
https://spark.apache.org/docs/3.0.1/api/python/pyspark.sql.htmldf.withColumn("email",concat(col("studentid"),\
lit("@mymail.sutd.edu.sg")))\
.show()+---------+-------+------+-----+--------------------+
|studentid| name|module|score| email|
+---------+-------+------+-----+--------------------+
| 100001| Ace| 50043| 90|[email protected]...|
| 100002|Brandon| 50043| 95|[email protected]...|
| 100003| Cheryl| 50043| 80|[email protected]...|
+---------+-------+------+-----+--------------------+
What happen when the newly created column's name clashes with an existing one?
df.filter(col("studentid") == "100003").show()+---------+------+------+-----+
|studentid| name|module|score|
+---------+------+------+-----+
| 100003|Cheryl| 50043| 80|
+---------+------+------+-----+
df.filter(col("score") > 90).show()+---------+-------+------+-----+
|studentid| name|module|score|
+---------+-------+------+-----+
| 100002|Brandon| 50043| 95|
+---------+-------+------+-----+
lit() is optional here, pyspark inserts it for us.
df.groupBy("module").avg().show()+------+-----------------+
|module| avg(score)|
+------+-----------------+
| 50043|88.33333333333333|
+------+-----------------+
moddata = [("50043", "Database and Big Data Systems")]
distmodData = sc.parallelize(moddata)
moddf = distmodData.toDF(["module", "modname"])
df.join(moddf, df["module"] == moddf["module"], "inner")\
.select(df["studentid"], df["name"], df["module"],\
df["score"], moddf["modname"]).show()+---------+-------+------+-----+--------------------+
|studentid| name|module|score| modname|
+---------+-------+------+-----+--------------------+
| 100001| Ace| 50043| 90|Database and Big ...|
| 100002|Brandon| 50043| 95|Database and Big ...|
| 100003| Cheryl| 50043| 80|Database and Big ...|
+---------+-------+------+-----+--------------------+
df.createOrReplaceTempView("students")
spark.sql("SELECT * FROM students").show()+---------+-------+------+-----+
|studentid| name|module|score|
+---------+-------+------+-----+
| 100001| Ace| 50043| 90|
| 100002|Brandon| 50043| 95|
| 100003| Cheryl| 50043| 80|
+---------+-------+------+-----+
With some notebook support, we can even use SQL to perform data visualization.
Machine learning!
MLLibpackageMLpackage
Spark MLLib is the original Machine Learning library that shipped with Spark
- supports RDD
- a simple set of data type and APIs
- Vector is one of the essential data structures for machine learning,
- In Spark, vectors are local data collections
- Dense vector - all values need to be specified.
from pyspark.mllib.linalg import *
dv = Vectors.dense(1.0, 0.0, 3.0) * Sparse vector - specify the size of
the vector as well as the non-zero values.
sv1 = Vectors.sparse(3, [0, 2], [1.0, 3.0]) # or
sv2 = Vectors.sparse(3, [(0, 1.0), (2, 3.0)])Labeled points are vectors with an assigned/labeled values. They are commonly used as the training data in algorithms such as logistic regression and SVM.
from pyspark.mllib.regression import *
# Create a labeled point with a positive label
# and a dense feature vector.
pos = LabeledPoint(1.0, Vectors.dense(1.0, 0.0, 3.0))
# Create a labeled point with a negative label
# and a sparse feature vector.
neg = LabeledPoint(0.0, Vectors.sparse(3, \
[(0, 1.0), (2, 3.0)]))Assuming
pos = ... # RDD of Labelpoints
neg = ... # RDD of labelpointsTraining the model
from pyspark.mllib.classification import SVMWithSGD
training = pos + neg
numIteration = 20
model = SVMWithSGD.train(training, numIterations)Inference
newInstance = Vectors.dense(1.0, 2.0, 3.0)
model.predict(newInstance)Spark ML is more recent development Machine Learning library that shipped with Spark
- support dataframes and dataset
- higher level API
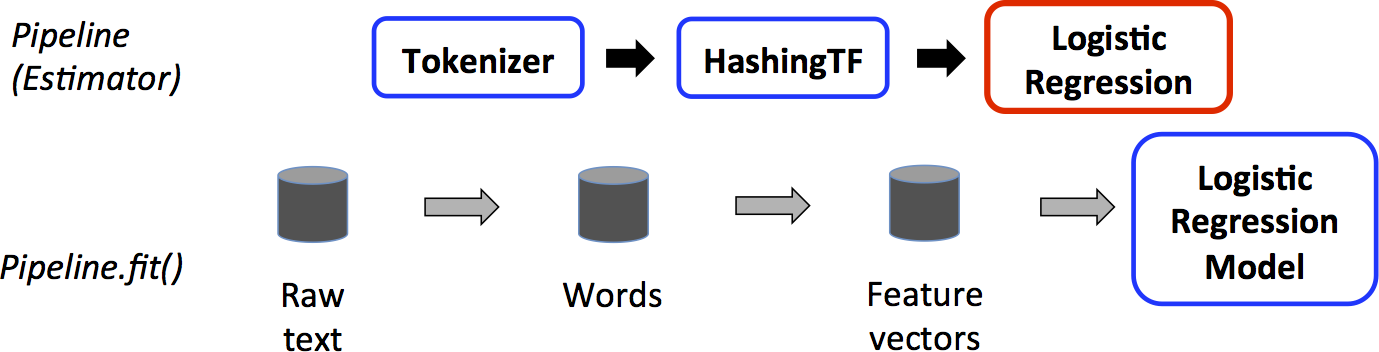
A Pipeline is a common name in machine learning frameworks. In Spark it represent a sequence of algos to process and/or learn data.
- Transformer - for data transformation, e.g. tokenization, TF-IDF
- Estimator - for model training, it fits weights in a model w.r.t to the training data and the objective functions
\scriptsize
from pyspark.ml import Pipeline, PipelineModel
from pyspark.ml.classification import LogisticRegression
from pyspark.ml.feature import HashingTF, Tokenizer
data = spark.createDataFrame([
(0, "a b c d e spark", 1.0),
(1, "b d", 0.0),
(2, "spark f g h", 1.0),
(3, "hadoop mapreduce", 0.0),
(4, "spark is scaling", 1.0),
(5, "random stuff", 0.0)
], ["id", "text", "label"])
train, test = data.randomSplit([0.8, 0.2], seed=12345)\scriptsize
# Configure an estimator pipeline,
tokenizer = Tokenizer(inputCol="text", outputCol="words")
hashingTF = HashingTF(inputCol=tokenizer.getOutputCol(), outputCol="features")
lr = LogisticRegression(maxIter=10, regParam=0.001)
pipeline = Pipeline(stages=[tokenizer, hashingTF, lr])
# Fit the pipeline to traini
model = pipeline.fit(train)\scriptsize
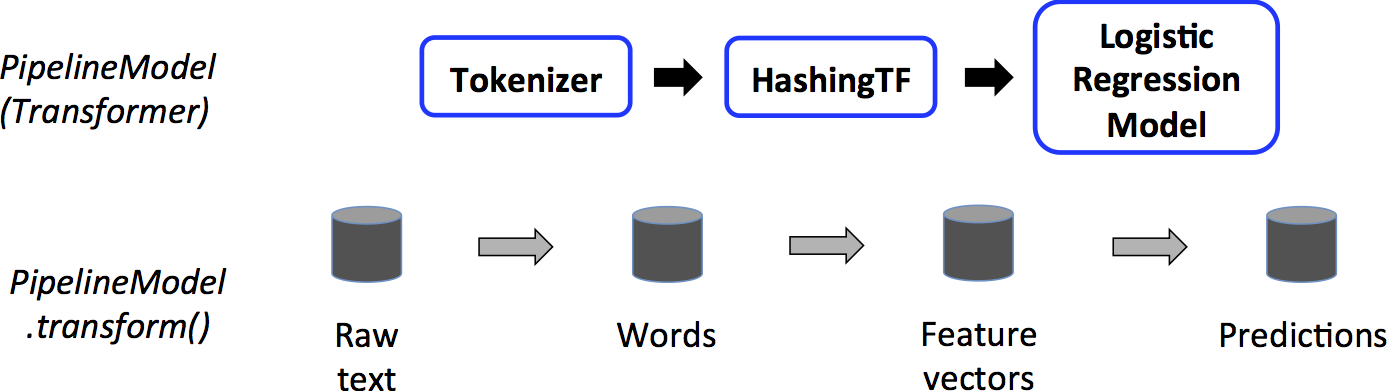
# Configure an Inference pipeline
# Note now model include tokenizerm hashingTF, and lr
pipeline_model = PipelineModel(stages=[model])
prediction = pipeline_model.transform(test)
result = prediction.select("id", "text", "probability", "prediction").collect()
print(result)More API references
https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/ml-guide.html- Why streaming?
- One of the 3 Vs of big data
- Near real-time
- Online-ML, trend analysis
- Requirement
- Scalable
- Fault tolerance
- Integration
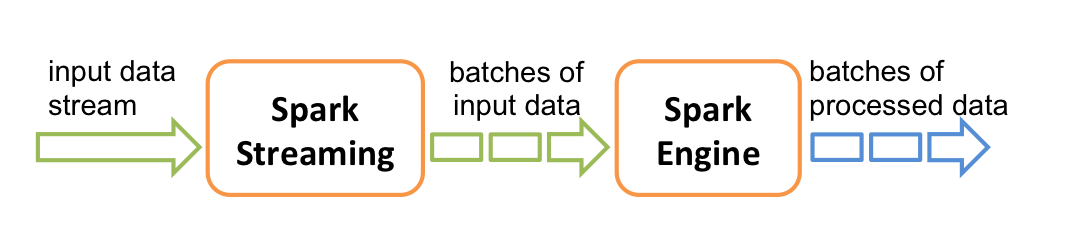
- Data stream chopped up to small batches
- Feed batches to Spark
- Called Discretized Stream (DStream)
from pyspark import SparkContext
from pyspark.streaming import StreamingContext
sc = SparkContext("local[2]", "PageView")
ssc = StreamingContext(sc, 1)
lines = ssc.socketTextStream("localhost", 9999)
pageViews = lines.map(lambda l:parse(l))
ones = pageViews.map(lambda x: (x.url, 1))
counts = ones.runningReduce(lambda x,y: x+y)- Spark architecture
- Spark Dataframe
- Spark MLLib and ML package
- Spark Streaming