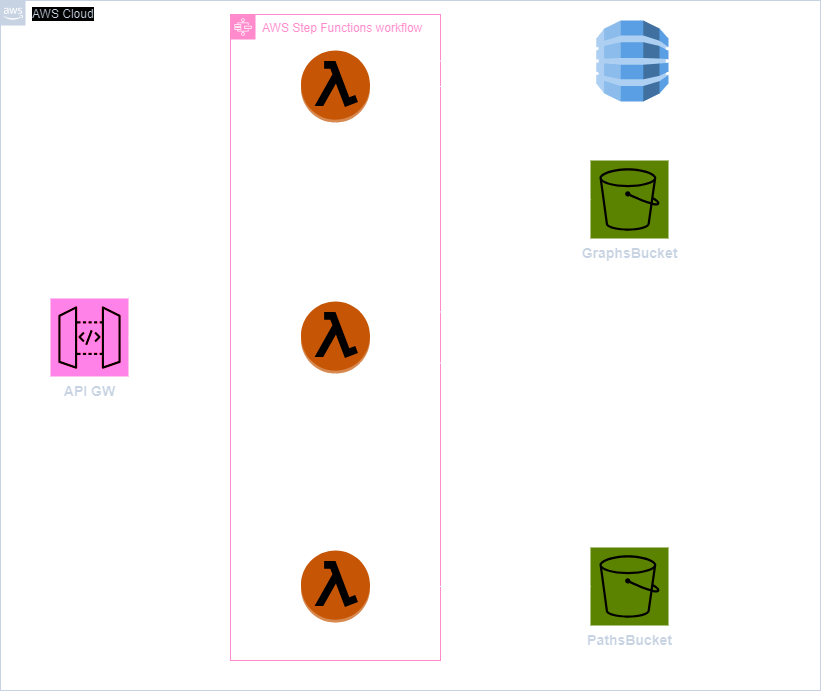
Deploy the stacks in the following order:
- DatabaseStack
- S3Stack
- SfnStack
- ApiStack
ApiStack outputs an endpoint to make queries.
Most of the time, if you're doing a new query, the lambda getGraph will first download the graph and send it to S3 for future queries. However, this step commonly take a long time (around 2-4 min, depending map size).
If you already has a list of pre-defined places where you will do the queries, you can fill the cities.json with the country and city of the place you'll query.
[
{
"country": "Germany",
"city": "Berlin",
},
...
]Notice that, you only have to put the city and country, then use the script fill_cities.py to modify this json with a lat and lon for a point in the city/country. Then, you can use the script upload_graph.py to download the graph and then upload it to S3 and Dynamo.
Algorithms are lambda functions implemented in Rust.
Classic graph-search algorithm, this algorithm only finds a path between the source and destination, it doesn't try to optimize the path in any way.
Classic graph path finding algorithm, instead of using a priority queue, it uses a heap, which in this scenario behaves similar. Dijkstra algorithm try to find the fastest path between source and destination. Notice that, it finds the fastest, not shortest, this is possible since the library osmnx provide information about the maximum speed allowed in an edge. Of course, this algorithm can also find the shortest, just set the maximum speed allowed to a constant value for all the edges.
Heuristic graph path finding algorithm, this algorithm improves dijkstra using a heuristic function that met some conditions. Classic heuristic the eulerian distance, which can be calculated from the latitude and longitude and using the haversine distance. A slightly modification is needed in order to use for fastest, in this case you can set a maximum speed along all the edges in the map, and then divide the distance with the maximum speed, so the heuristic is:
Shortest time between two nodes is the eulerian distance divided by the maximum speed
Maximum speed is not a constant value, and should be calculated for each graph, lower maximum speed leads to a better heuristic, this value is currently setted to 150.0 km/h.
I don't have a proof of the correctness of this algorithm modification, so it's probably that it can't even find a path, however in most cases it outperforms classic A*.
Store the graph information for a city and country.
{graphId}.graphml: Graph information fromnetworkxlibrary.*-{graphId}.json: Simple graph representation using only nodes and edges.
Store the results for a request.
*.json: Edges to plot in the graph*.png: Plot of the request
A request always generates a plot and three edges data: path, active, visited.
- Path edges are
edgesthat belongs to thefastestpath. - Active edges are
edgesthat are going to be processed for the algorithm. - Visited edges are
edgesalready processed by the algorithm.