The open-source TypeScript platform for autonomous AI agents and LLM based workflows
Nous (Greek: νοῦς) is a term from classical philosophy often associated with intellect or intelligence, represents the human mind's capacity to comprehend truth and reality.Home | Setup | Observability | Function calling | Autonomous AI Agent | AI Software Engineer | AI Code reviews | Tools/Integrations | Roadmap
The Nous Story | Features | UI Examples | Code examples | Contributing
Nous started from a simple goal: to harness AI's potential to enhance real-world productivity, born in DevOps and Platform Engineering space. We envisioned a tool that could:
- Automate various processes and support requests, and triage build failures.
- Review code for compliance with standards and best practices.
- Assist with large refactorings, and more.
At TrafficGuard we process billions of events a month for our global clients, increasing their ad spend ROI by protecting against bots and other forms of invalid traffic. Our SaaS on GCP comprises projects developed in TypeScript, Python, GoogleSQL, PHP and Terraform, deployed from GitLab.
With open source projects typically Python/GitHub focused, and the vendor AI tools being focused in their silos, we saw a need for TypeScript based tooling which can work across our entire tech stack, and understand the overall architecture.
Through its evolution we've designed nous as a flexible platform for the TypeScript community to expand and support the use cases and integrations of your choice.
Our design choice of Firestore for the initial database implementation, with Cloud Run, provides a scale-to-zero solution with zero-cost using the free tier. With the intention to support uses cases such as your own custom personal assistant, always available via mobile.
Key features include:
- Advanced autonomous agents
- Reasoning/planning inspired from Google's Self-Discover paper
- Memory and function call history for complex, multi-step workflows
- Adaptive iterative planning with hierarchical task decomposition
- Two control-loop function calling options (LLM-independent):
- Custom XML-based function calling
- Dynamic code generation with sandboxed execution for multistep function calling and logic
- Opportunistically can significantly reduce cost and latency over LLM-native/XML function calling
- LLM function schemas auto-generated from source code
- Function callable integrations:
- Filesystem, Jira, Slack, Perplexity, Gitlab, GitHub and more
- Supports multiple LLMs/Services:
- OpenAI, Anthropic (native & Vertex), Gemini, Groq, Fireworks, Together.ai, DeepSeek, Ollama
- CLI and Web interface
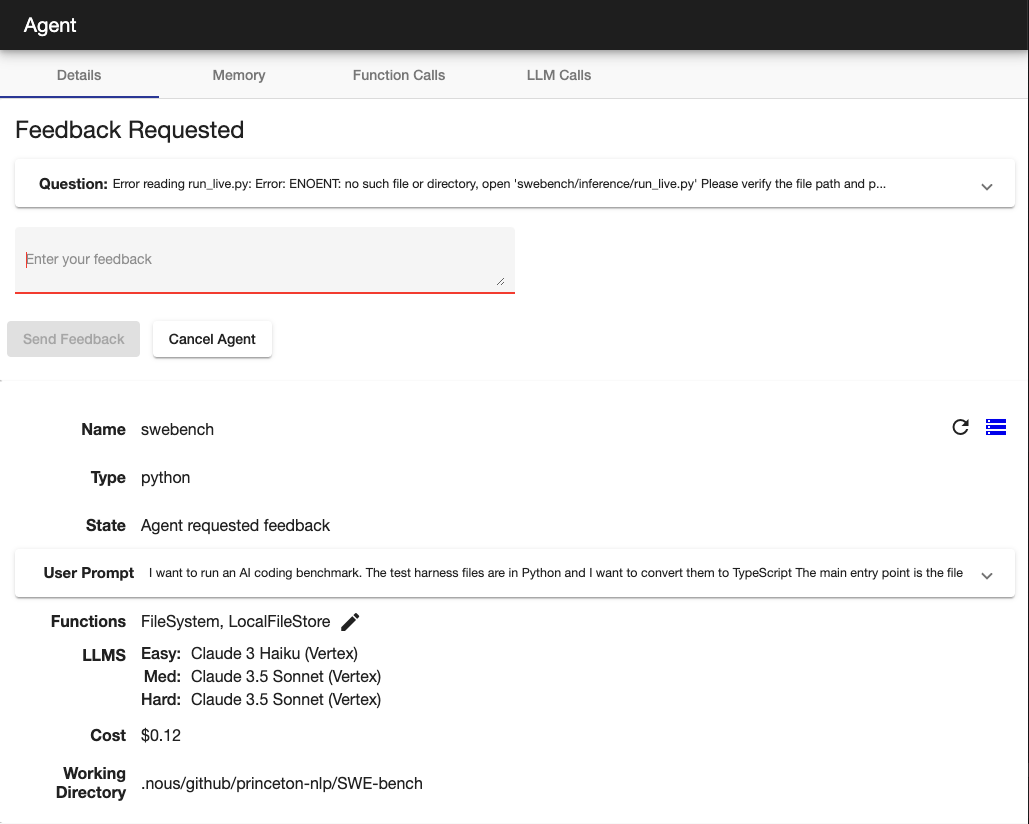
- Human-in-the-loop for:
- Budget control
- Agent initiated questions
- Error handling
- Flexible deployment options:
- Run locally from the command line or through the web UI
- Scale-to-zero deployment on Firestore & Cloud Run
- Multi-user SSO enterprise deployment (with Google Cloud IAP)
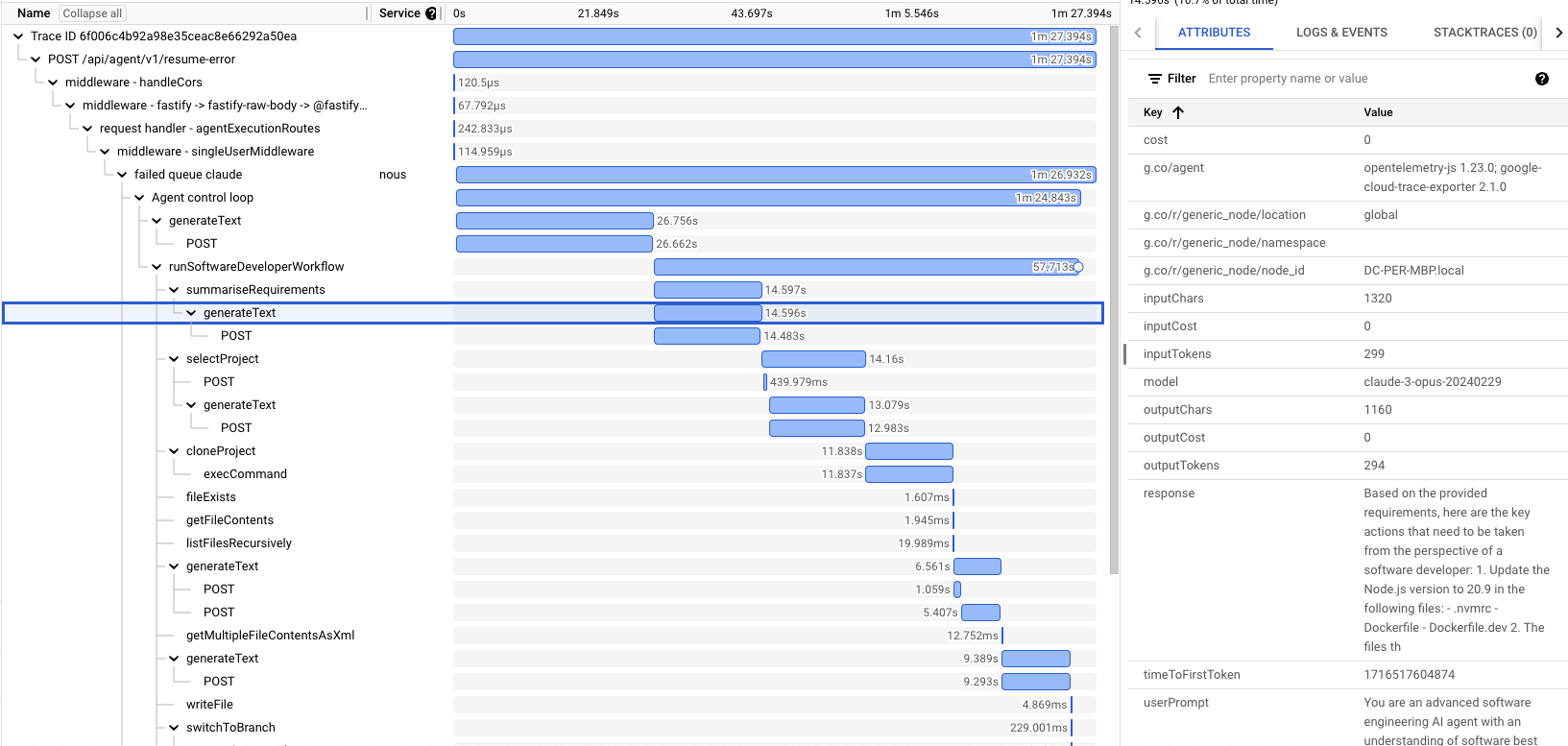
- Observability with OpenTelemetry tracing
- Code Editing Agent:
- Auto-detection of project initialization, compile, test and lint
- Find the relevant files to edit and perform initial analysis
- Code editing loop with compile, lint, test, fix (editing delegates to Aider)
- Compile error analyser can search online, add additional files and packages
- Software Engineer Agent:
- Find the appropriate repository from GitLab/GitHub
- Clone and create branch
- Call the Code Editing Agent
- Create merge request
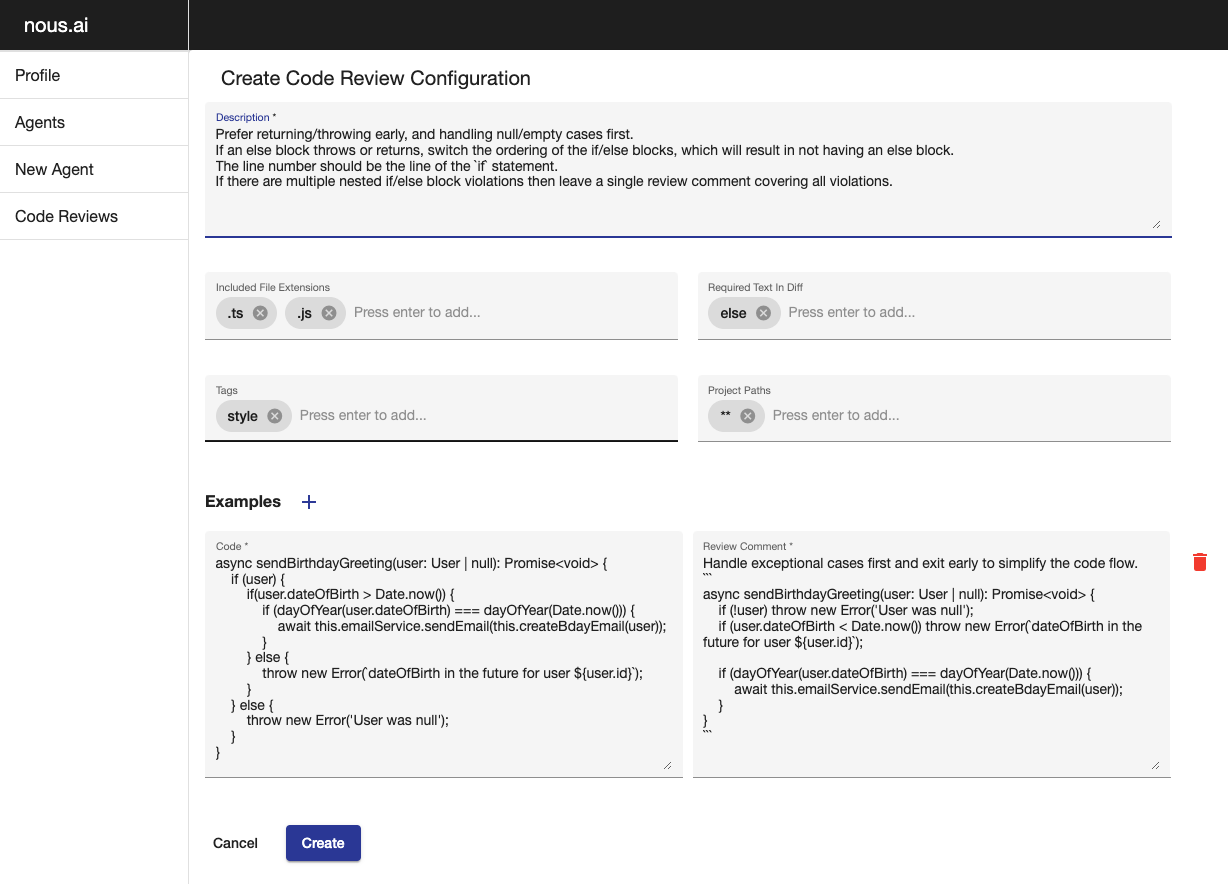
- Code Review agent:
- Configurable code review guidelines
- Posts comments on GitLab merge requests at the appropriate line with suggested changes
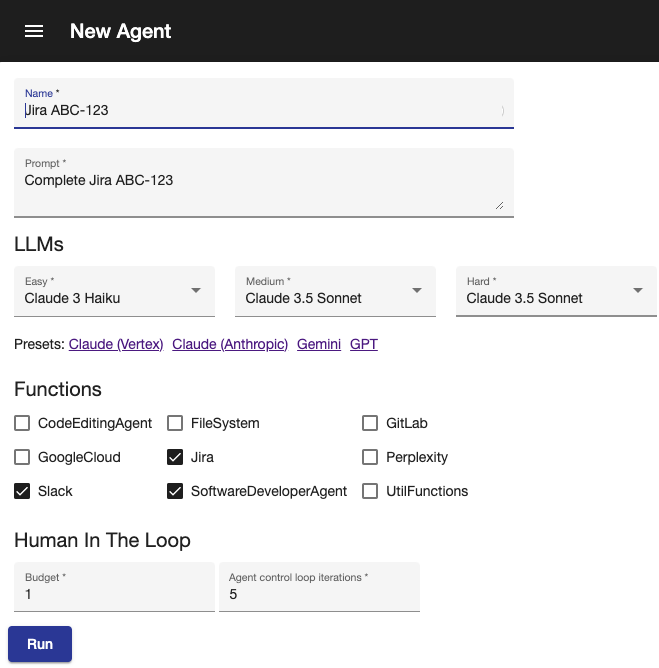
New Agent | Sample trace | Human in the loop notification | Agent requested feedback | List agents | Code review config
Nous doesn't use LangChain, for many reasons that you can read online
Let's compare the LangChain document example for Multiple Chains to the equivalent Nous implementation.
import { PromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts";
import { RunnableSequence } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
import { StringOutputParser } from "@langchain/core/output_parsers";
import { ChatAnthropic } from "@langchain/anthropic";
const prompt1 = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate(
`What is the city {person} is from? Only respond with the name of the city.`
);
const prompt2 = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate(
`What country is the city {city} in? Respond in {language}.`
);
const model = new ChatAnthropic({});
const chain = prompt1.pipe(model).pipe(new StringOutputParser());
const combinedChain = RunnableSequence.from([
{
city: chain,
language: (input) => input.language,
},
prompt2,
model,
new StringOutputParser(),
]);
const result = await combinedChain.invoke({
person: "Obama",
language: "German",
});
console.log(result);import { llms } from '#agent/context'
import { anthropicLLMs } from '#llms/anthropic'
const prompt1 = (person: string) => `What is the city ${person} is from? Only respond with the name of the city.`;
const prompt2 = (city: string, language: string) => `What country is the city ${city} in? Respond in ${language}.`;
runAgentWorkflow({ llms: anthropicLLMs() }, async () => {
const city = await llms().easy.generateText(prompt1('Obama'));
const result = await llms().easy.generateText(prompt2(city, 'German'));
console.log(result);
});The Nous code also has the advantage of static typing with the prompt arguments, enabling you to refactor with ease. Using simple control flow allows easy debugging with breakpoints/logging.
To run a fully autonomous agent:
startAgent({
agentName: 'Create ollama',
initialPrompt: 'Research how to use ollama using node.js and create a new implementation under the llm folder. Look at a couple of the other files in that folder for the style which must be followed',
functions: [FileSystem, Perplexity, CodeEditinAgent],
llms,
});The Nous code also has the advantage of static typing with the prompt arguments, enabling you to refactor with ease. Using simple control flow allows easy debugging with breakpoints/logging.
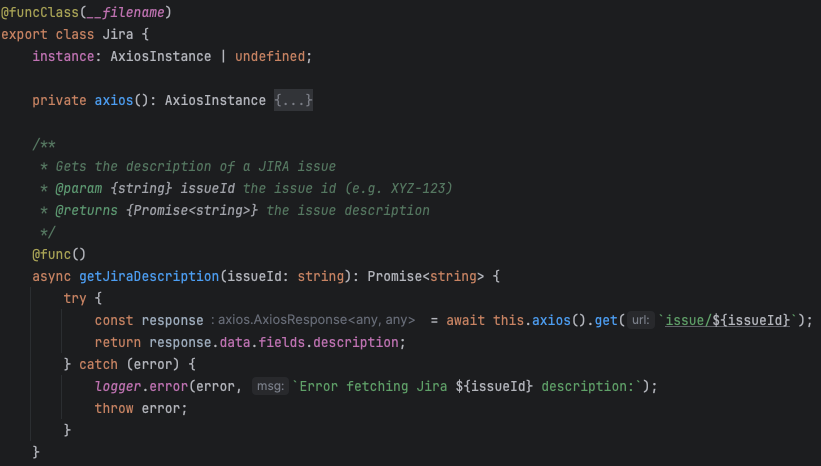
LLM function calling schemas are automatically generated by having the @func decorator on class methods.
Visit our documentation site for the getting started guide and more details.
We warmly welcome contributions to the project through issues, pull requests or discussions
Contributed by TrafficGuard - Increasing the ROI on your ad spend.
Reach out to us as [email protected] if you'd like support to ramp up as a contributor.