-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 185
01. WiFi Basics
-
Station (STA) = Client device connecting to AP.
-
Access Point (AP) = Networking hardware providing stations access to network.
-
Extended Service Set (ESS) = Infrastructure Network. ESS is comprised of one or more BSS, joined together by a common DS.
-
Distribution System (DS) = Link APs together in an ESS.
-
Independent Basic Service Set (IBSS) = "Ad-Hoc" Network. Do not require an AP, consists of at least one station.
-
Basic Service Set (BSS) = AP inside ESS.
-
BSSID = MAC address of BSS (AP).
-
ESSID = Name of ESS (identify a wireless network).
-
Card's Transmit (TX) Power =
- How far the card can transmit.
- Expressed in mW or dBm.
-
dBm = 10*log_10(mW). 1 mW = 1 dBm, 10 mW = 10 dBm, 100 mW = 20 dBm, 1W = 30 dBm... - For example, Alfa AWUS306H has TX power = 1000mW (30dBm)
-
Card's Sensitivity =
- How well it can receive.
- Often overlooked in favor of TX Power.
- Usually measured in dBm.
- The more negative number, the better.
- Typical values for sensitivity in average cards = -80 to -90 dBm.
- Every -3dBm = double sensitivity.
-
Antenna's Sensitivity =
- Measured in dBi.
- Increase of 3 dBi = double antenna's effective range.
| Spectrum | Year | Max Speed | Distance | Channel Bandwidth | Frequency | Congestion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 802.11a | 1999 | 54 Mbps | 35m | 20 MHz | 5 GHz | Low |
| 802.11b | 1999 | 11 Mbps | 35m | 22 MHz | 2.4 GHz | High |
| 802.11g | 2003 | 54 Mbps | 38m | 20 MHz | 2.4 GHz | High |
| 802.11n | 2009 | 300/900 Mbps | 70m/35m | 20/40 MHz | 2.4 / 5 GHz | High/Low |
| 802.11ac | 2013 | 1300 Mbps | 35m | 20/40/80/160 MHz | 2.4 / 5 GHz | Low |
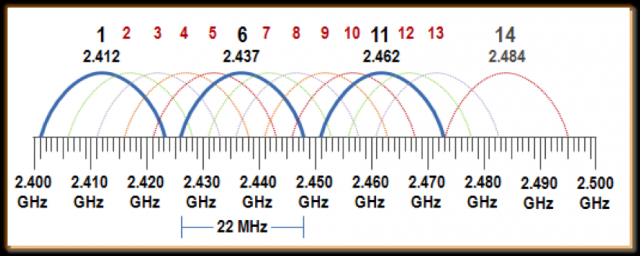
- Each channel is allotted 20MHz, separated by 5MHz
- Total bandwidth = 100MHz
- 11 Channels
- Channels overlap with each other => cause interferences
- Some channels have better WiFi performance than others because they are non-overlapping => Channels 1, 6, 11 are non-overlapping
- WiFi coverage better than 5GHz because lower frequencies can more easily penetrate solid objects
- Non-WiFi interfence possible (e.g. Bluetooth)
- Universal compatibility: 802.11 b/g/n
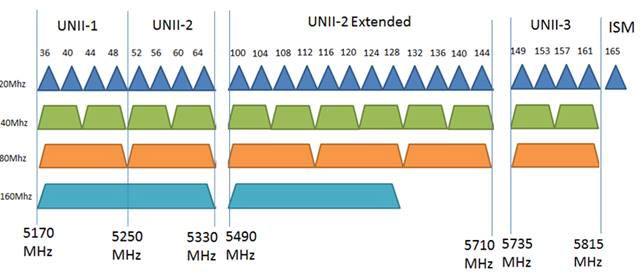
- 45 Channels
- 24 non-overlapping channels
- Speed up to 1300 Mbps (faster than 2.4 GHz)
- Lower indoor rate
- Limited compatibility: 802.11 a/n/ac
- Very little non-WiFi interference
- WiFi standard allows channel bandwidths of 10, 20, 22, 40, 80 and 160 MHz, but 10MHz is not used anymore.
- 80 MHz and 160 MHz can be used only with 5 GHz frequency.
- Certain devices are not being able to connect to APs with channel widths > 40Mhz.
- By default, the 2.4 GHz frequency uses a 20 MHz channel width.
- 20MHz channel width is wide enough to span one channel.
- 40 MHz channel width bonds two neighbouring 20 MHz channels together, forming a 40 MHz channel width
=> greater speed and faster transfer rates. In this case, there are:
- One "control" channel functions as the main channel: This main channel is used to send Beacon packets & data packets.
- One "auxiliary" channel (or extension channel): It is used to send other packets. The extension channel has to be contiguous with the edge of the control channel, without overlapping.
- Notation for 40 MHz channel:
- HT40+ = Means that the frequency of the main ("control") channel is higher than the auxiliary channel. Warning: In this case, the main channel cannot be 1 because it would mean that "auxiliary" channel would be out of allowed frequency for the 2.4GHz band !
- HT40- = Otherwise.
- HT20 High Throughput 20MHz, 802.11n
- HT40 High Throughput 40MHz, 802.11n
- HT40- High Throughput 40MHz, 802.11n, control channel is bellow extension channel.
- HT40+ High Throughput 40MHz, 802.11n, control channel is above extension channel.
- VHT20 Very High Throughput 20MHz, Supported by 802.11ac
- VHT40 Very High Throughput 40MHz, Supported by 802.11ac
- VHT80 Very High Throughput 80MHz, Supported by 802.11ac
- VHT160 Very High Throughput 160MHz, Supported by 802.11ac
Ref: https://openwrt.org/docs/guide-user/network/wifi/basic#htmodethe_wi-fi_channel_width
Cf. https://gist.github.com/W00t3k/f494d8cd5cdf34a3e0cab8249bf402f1#file-kali-supported-usb-devices-csv
- 01. WiFi Basics
- 02. 802.11 Specifications
- 03. WPS (WiFi Protected Setup)
- 04. WPA Protocol Overview
- 05. WPA/WPA2 Personal (PSK) Authentication
- 06. WPA/WPA2 PSK Traffic Decryption
- 07. WPA/WPA2 Enterprise (MGT)
- 08. Evil Twin Attacks
- 09. 802.11 Network Selection Algorithms
- 01. WiFi Interfaces Management
- 02. WiFi Connection
- 03. WiFi Monitoring (Passive Scanning)
- 04. Hotspot Captive Portal Bypass
- 05. WiFi Denial of Service
- 06. WEP Authentication Cracking
- 07. WPA/WPA2 Personal (PSK) Authentication Cracking
- 08. WPA/WPA2 Enterprise (MGT) Authentication Cracking
- 09. WPA/WPA2 Personal (PSK) Traffic Decryption
- 10. Basic AP (Manual Configuration)
- 11. Open Network (no passphrase) Rogue AP / Evil Twin
- 12. WPA/WPA2 Personal (PSK) Rogue AP / Evil Twin
- 13. WPA/WPA2 Enterprise (MGT) Rogue AP / Evil Twin