-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 6
IncrementalModel_step4
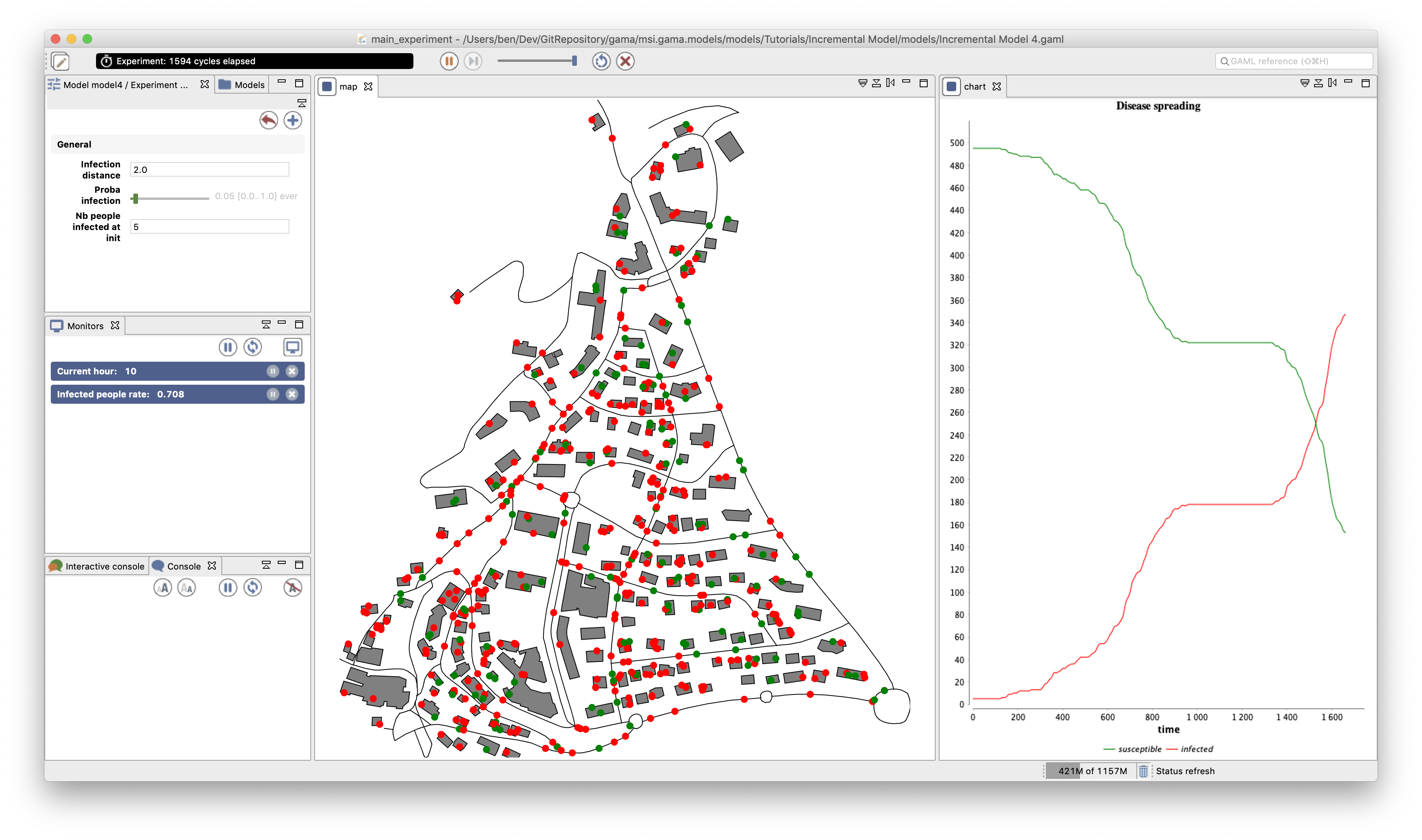
This step illustrates how to load a graph and use it for the displacement of our agents.
- Definition of a global graph to represent the road network.
- Definition of a new global variable:
staying_coeffto represent the fact that people move more near 9h, 12h, and 18h. - Definition of two new variables for the people agents:
targetandstaying_counter(to manage their mobility). - Definition of a new reflex for people agents:
stay. - Modification of the
movereflex of the people agents.
We define two new global variables:
-
road_network(graph): represents the graph built from the road network. -
staying_coeff(float): represents the fact that people have more chance to move from their current building near 9h (go to work), 12h (lunchtime) and 18h (go home). This variable is updated at each simulation step (using theupdatefacet).
global{
....
graph road_network;
float staying_coeff update: 10.0 ^ (1 + min([abs(current_date.hour - 9), abs(current_date.hour - 12), abs(current_date.hour - 18)]));
....
}
We need to compute from the road agents, a graph for the moving of the people agents. The operator as_edge_graph allows doing that. It automatically builds from a set of agents or geometries a graph where the agents are the edges of the graph, a node represent the extremities of the agent geometry. The weight of each edge corresponds to the length of the road.
global {
...
init {
...
create road from: roads_shapefile;
road_network <- as_edge_graph(road);
...
}
}
First, we add two new variables for the people agents:
-
target(point): the target location that the people want to reach (a point inside a building). -
staying_counter(int): the number of cycles since the agent arrived at its building.
We define a new reflex named stay that is activated when the agent has no target (target = nil), i.e. when the agent is inside a building. This reflex increments the staying_counter, then it tests the probability to leave that is computed from the staying_counter (longer the agent is inside the building, more it has a chance to leave) and the staying_coeff (closer to 9h, 12h, and 18h, more the agent has a chance to leave).
If the agents decide to leave, it computes a new target as a random point inside one of the buildings (randomly chosen).
species people skills: [moving] {
...
reflex staying when: target = nil {
staying_counter <- staying_counter + 1;
if flip(staying_counter / staying_coeff) {
target <- any_location_in (one_of(building));
}
}
...
}
We modify the move reflex. Now, this reflex is activated only when the agent has a target (target != nil). In this case, the agent moves toward its target using the built-in goto action. Note that we specified a graph (road_network) to constraint the moving of the agents on the road network with the facet on. The agent uses the shortest path (according to the graph) to go to the target point. When the agent arrives at destination (location = location), the target is set to nil (the agent will stop moving) and the staying_counter is set to 0.
species people skills:[moving]{
...
reflex move when: target != nil{
do goto target: target on: road_network;
if (location = target) {
target <- nil;
staying_counter <- 0;
}
}
}
https://github.com/gama-platform/gama.old/blob/GAMA_1.9.2/msi.gama.models/models/Tutorials/Incremental%20Model/models/Incremental%20Model%204.gaml
- Installation and Launching
- Workspace, Projects and Models
- Editing Models
- Running Experiments
- Running Headless
- Preferences
- Troubleshooting
- Introduction
- Manipulate basic Species
- Global Species
- Defining Advanced Species
- Defining GUI Experiment
- Exploring Models
- Optimizing Models
- Multi-Paradigm Modeling
- Manipulate OSM Data
- Cleaning OSM Data
- Diffusion
- Using Database
- Using FIPA ACL
- Using BDI with BEN
- Using Driving Skill
- Manipulate dates
- Manipulate lights
- Using comodel
- Save and restore Simulations
- Using network
- Headless mode
- Using Headless
- Writing Unit Tests
- Ensure model's reproducibility
- Going further with extensions
- Built-in Species
- Built-in Skills
- Built-in Architecture
- Statements
- Data Type
- File Type
- Expressions
- Exhaustive list of GAMA Keywords
- Installing the GIT version
- Developing Extensions
- Introduction to GAMA Java API
- Using GAMA flags
- Creating a release of GAMA
- Documentation generation