-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 6
PredatorPrey_step4
This fourth step illustrates how to monitor more precisely the simulation. Practically, we will define monitors to follow the evolution of specific variables (or expressions) whereas inspectors allow the user to follow the state of a given agent (or a species).
- Adding of a monitor to follow the evolution of the number of prey agents
We add a new global variable:
-
nb_preys: returns, each time it is called, the current number of (live) prey agents
To do so we use the ->{expression} facet which returns the value of expression, each time it is called.
We use as well the operator length that returns the number of elements in a list.
Thus, in the global section, we add the nb_preys global variable:
int nb_preys -> {length (prey)};
A monitor allows users to follow the value of an arbitrary expression in GAML. It has to be defined in an output section. A monitor is defined as follows:
monitor monitor_name value: an_expression refresh: every(nb_steps);
With:
-
value: mandatory, that value will be displayed in the monitor. -
refresh: bool, optional: if the expression is true, compute (default is true).
In this model, we define a monitor to follow the value of the variable nb_preys:
monitor "number of preys" value: nb_preys;
Inspectors allow to obtain information about a species or an agent. There are two kinds of agent information features:
- Species browser: provides information about all the agents of a species. Available in the Agents menu.
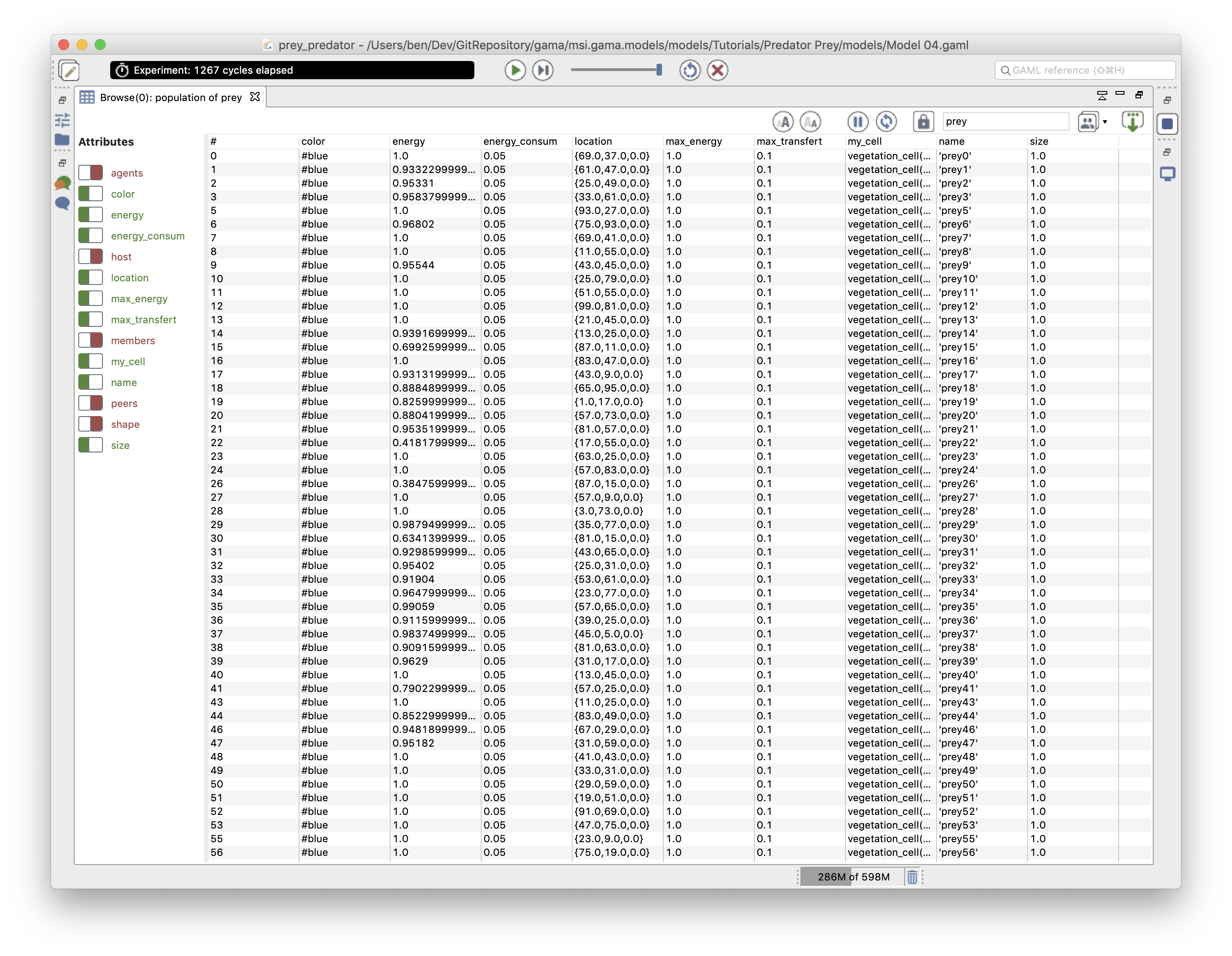
- Agent inspector: provides information about one specific agent. Also allows to change the values of its variables during the simulation. Available from the Agents menu, by right_clicking on a display, in the species inspector, or when inspecting another agent. It provides also the possibility to «highlight» the inspected agent.
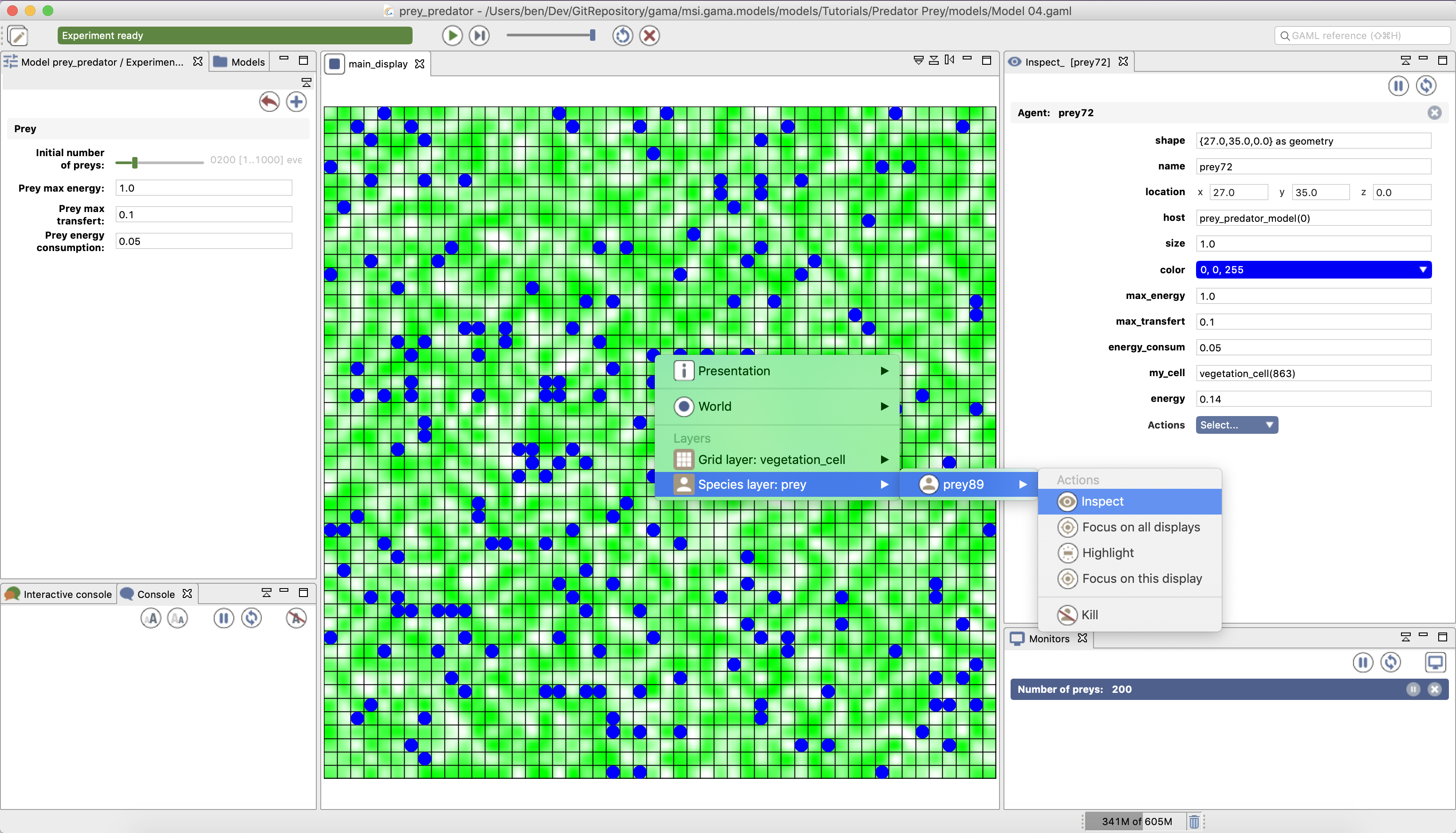
https://github.com/gama-platform/gama.old/blob/GAMA_1.9.2/msi.gama.models/models/Tutorials/Predator%20Prey/models/Model%2004.gaml
- Installation and Launching
- Workspace, Projects and Models
- Editing Models
- Running Experiments
- Running Headless
- Preferences
- Troubleshooting
- Introduction
- Manipulate basic Species
- Global Species
- Defining Advanced Species
- Defining GUI Experiment
- Exploring Models
- Optimizing Models
- Multi-Paradigm Modeling
- Manipulate OSM Data
- Cleaning OSM Data
- Diffusion
- Using Database
- Using FIPA ACL
- Using BDI with BEN
- Using Driving Skill
- Manipulate dates
- Manipulate lights
- Using comodel
- Save and restore Simulations
- Using network
- Headless mode
- Using Headless
- Writing Unit Tests
- Ensure model's reproducibility
- Going further with extensions
- Built-in Species
- Built-in Skills
- Built-in Architecture
- Statements
- Data Type
- File Type
- Expressions
- Exhaustive list of GAMA Keywords
- Installing the GIT version
- Developing Extensions
- Introduction to GAMA Java API
- Using GAMA flags
- Creating a release of GAMA
- Documentation generation