-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 6
InstallingPlugins
Besides the plugins delivered by the developers of the GAMA platform, there are a number of additional plugins that can be installed to add new functionalities to GAMA or enhance the existing ones. GAMA being based on Eclipse, a number of plugins developed for Eclipse are then available (a complete listing of Eclipse plugins can be found in the so-called Eclipse MarketPlace).
There are, however, three important restrictions:
- The current version of GAMA is based on Eclipse 2022-12 (version number 4.26.0), which excludes de facto all the plugins targeting solely a specific different version of Eclipse. These will refuse to install anyway.
- The Eclipse foundations in GAMA are only a subset of the complete Eclipse platform, and a number of libraries or frameworks (for example the Java Development Toolkit) are not (and will never be) installed in GAMA. So plugins relying on their existence will refuse to install as well.
- Some components of GAMA rely on a specific version of other plugins and will refuse to work with other versions, essentially because their compatibility will not be ensured anymore. For instance, the parser and validator of the GAML language in GAMA 1.9.2 require XText v. 2.29.0 to be installed.
With these restrictions in mind, it is, however, possible to install interesting additional plugins. We propose here a list of some of these plugins (known to work with GAMA), but feel free to either add a comment if you have tested plugins not listed here or create an issue if a plugin does not work, in order for us to see what the requirements to make it work are and how we can satisfy them (or not) in GAMA.
Installing new plugins is a process identical to the one described when updating GAMA, with one exception: the update site to enter is normally provided by the vendor of the additional plugin and must be entered instead of GAMA's one in the dialog.
Let suppose that we want to install a GAMA plugin developed in order to allow GAMA to ask R to do some computations. This plugin is developed by the GAMA community, but the installation of any plugin will be similar, only the address of the update site will change. To install this plugin, open the pane to install new plugins: "Help > Install new plugins ... ".
Choose in the "Work with..." text field:
msi.gama.experimental.p2updatesite - http://updates.gama-platform.org/experimental
If it is not available, you can simply type the address of the update site in the text field:
http://updates.gama-platform.org/experimental/<GAMA-VERSION>
Note: The
<GAMA-VERSION>should be replaced by the version of GAMA you are using.For example, current latest version is GAMA 1.9.2, then the address is this :
http://updates.gama-platform.org/experimental/1.9.2
Among all the plugins, select RJava in the category "Optional components of GAMA" and click on "Next >" button.
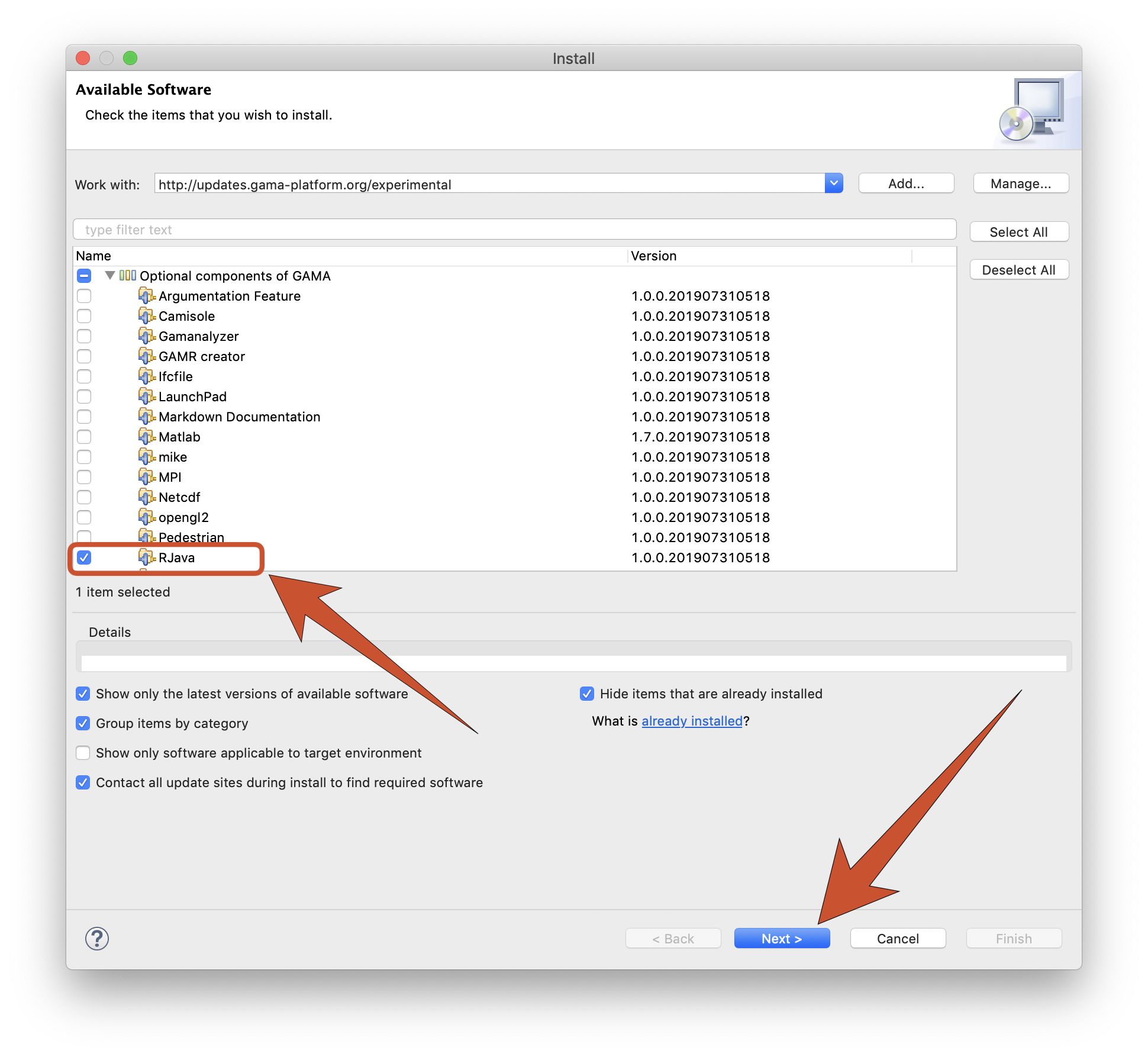
The initial dialog is followed by two other ones, a first to report that the plugin satisfies all the dependencies, a second to ask the user to accept the license agreement.
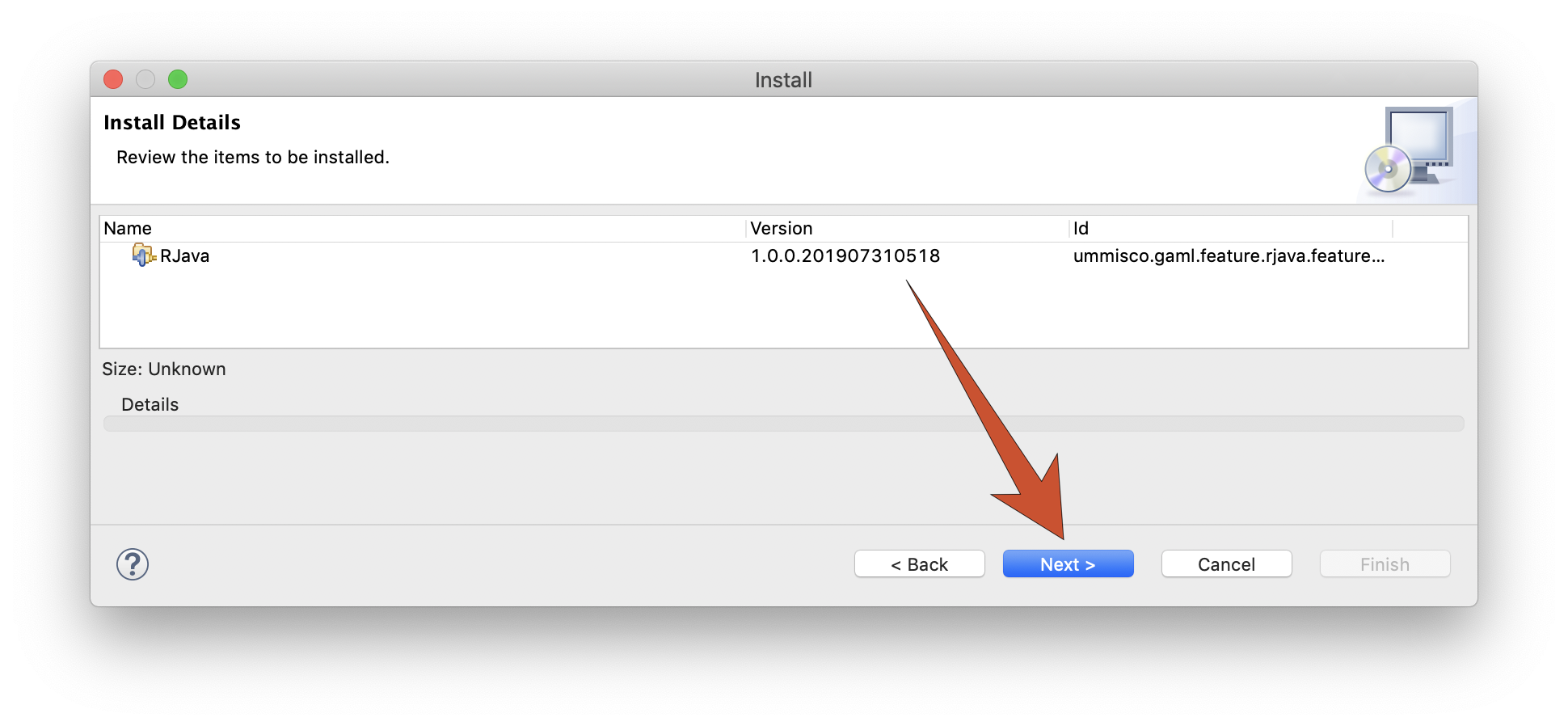
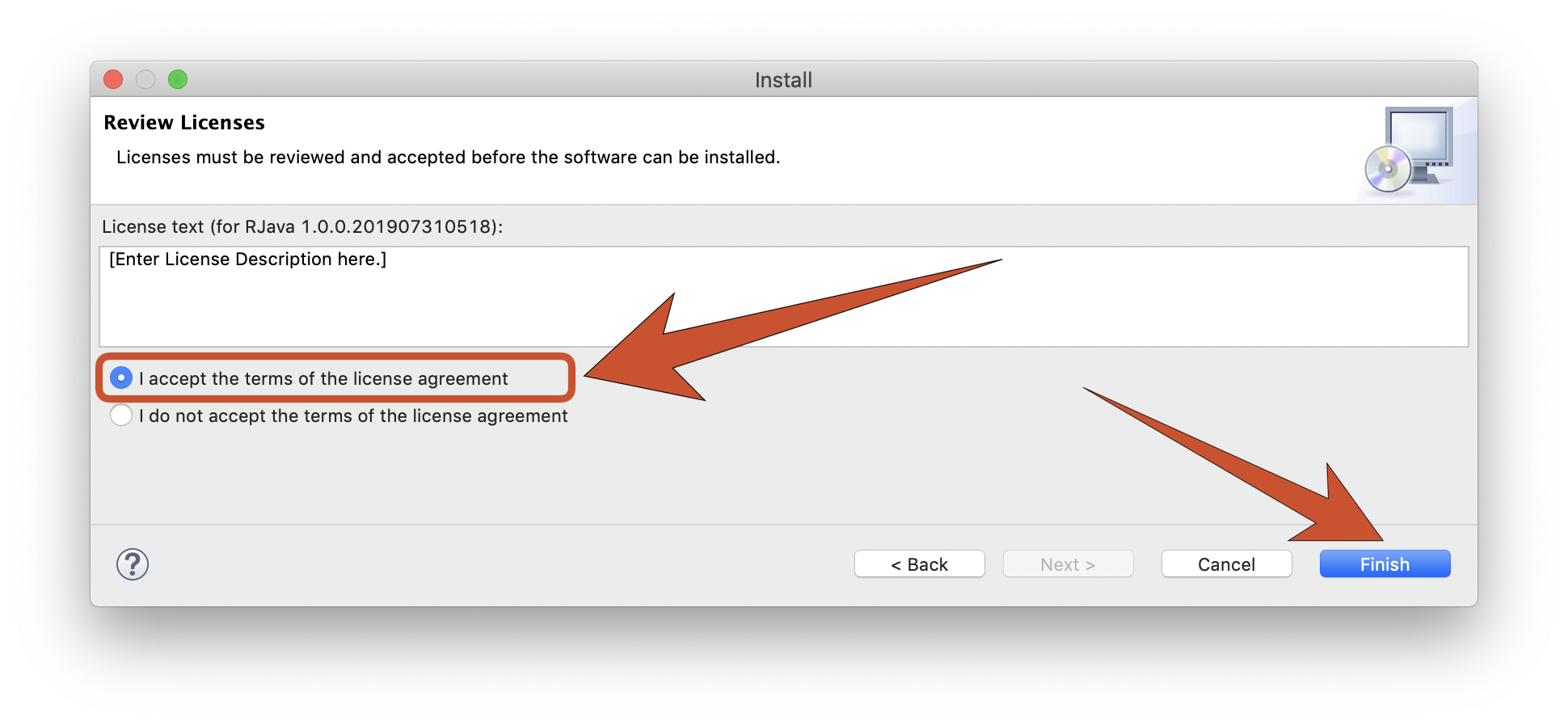
Once we dismiss the warning that the plugin is not signed and accept to restart GAMA, we can test the new plugin.
In the case of plugins extending the features of GAMA, some example models are often provided with the new plugins to illustrate its use (and it is the case for RJava). These new models are accessible in GAMA from Plugin models in a dedicated folder (GAMA to Rjava in the case of RJava). We may need to refresh the model library to let it appear. Notice that you need to configure GAMA to access R before running these models.
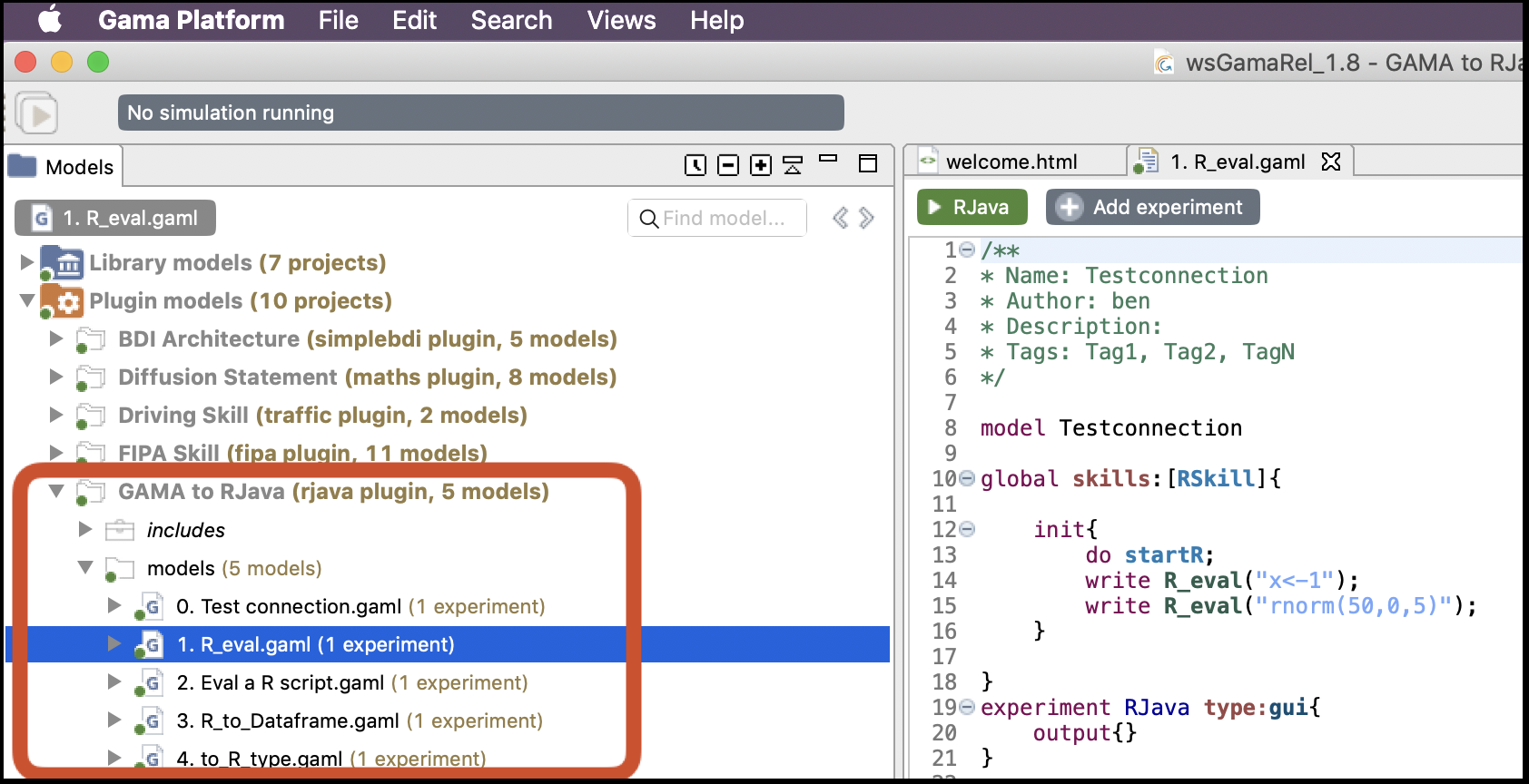
The update site located at the address http://updates.gama-platform.org/experimental contains new plugins for GAMA mainly developed by the GAMA community (its Github repository is available here). As the name of the repository highlights it, these plugins are most of them still in development, before integration in the kernel of GAMA.
There are more and more applications of GAMA for participative simulations (LittoSim, MarakAir, HoanKiemAir...). There was thus a need for new features to improve the possible interactions with simulations and the definition of the Graphical User Interface. The two plugins Remote.Gui and Gaming (available in the "Participative simulation" category) attempts to fill this need.
-
Remote.Guiallows exposing some model parameters, in order that they can be modified through a network. This allows, for example, to develop a remote application (e.g. Android application) to control the parameters' values during the simulation. -
Gamingallows the modeler to define displays that are much more interactive. This is used to define serious games in which the users can have a wide range of possible interactions with the simulation.
This plugin allows the modeler to launch some computation on the R software. To this purpose, R should be installed on your computer and GAMA should be properly configured.
This possible connection to R opens thus the possibility for the modeler to use all the statistical functions and libraries developed in this tool of reference. In addition, R scripts defined by the modeler can also be used directly from his/her GAMA model.
Similarly to RJava, Matlab and Weka plugins allow the modeler to run computations on the Matlab and Weka software, taking advantages of all the possibilities of these softwares and of scripts defined by him/herself.
Notice that the Matlab plugin requires that MATLAB 2019a is installed and activated on your computer.
- Installation and Launching
- Workspace, Projects and Models
- Editing Models
- Running Experiments
- Running Headless
- Preferences
- Troubleshooting
- Introduction
- Manipulate basic Species
- Global Species
- Defining Advanced Species
- Defining GUI Experiment
- Exploring Models
- Optimizing Models
- Multi-Paradigm Modeling
- Manipulate OSM Data
- Cleaning OSM Data
- Diffusion
- Using Database
- Using FIPA ACL
- Using BDI with BEN
- Using Driving Skill
- Manipulate dates
- Manipulate lights
- Using comodel
- Save and restore Simulations
- Using network
- Headless mode
- Using Headless
- Writing Unit Tests
- Ensure model's reproducibility
- Going further with extensions
- Built-in Species
- Built-in Skills
- Built-in Architecture
- Statements
- Data Type
- File Type
- Expressions
- Exhaustive list of GAMA Keywords
- Installing the GIT version
- Developing Extensions
- Introduction to GAMA Java API
- Using GAMA flags
- Creating a release of GAMA
- Documentation generation